greenspecR&D
Confocal MicroScope
Confocal MicroScope
-
NS - 3000

-
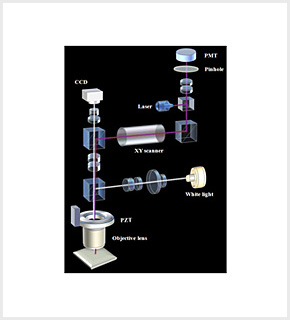
Structure diagram
Measurement Examples
-
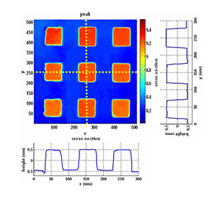
Height map and cross-sectionsof standard sample
(VLSI, step height=0.94um) -

3-Dimensional View of the surface profile
-

Sharp defect near column spacer
-
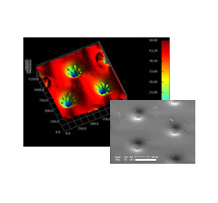
BLU Panel
-
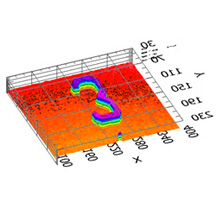
Micro patterned structure
-
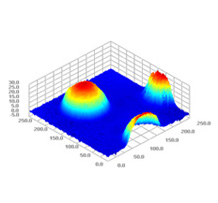
Wafer bump
-
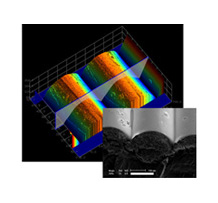
Light Guide Panel
-

Wire Bonding
-

Touch Panel Dot Spacer
-

Ultrathin Coating Step
-

ITO File Surface
-

LCD Column spacer
-

Laser Scribing of PV Panel
-
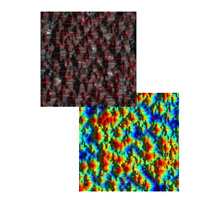
Pyramid Texture of PV
-
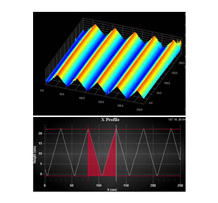
Grating Plate
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) 기본 원리
-
- • Optical Sectioning 3D im aging
- - depth discrimination
-
- • Improved SNR (signal to noise ratio)
- - out-of-focus blur rejection
-
- • Improved lateral resolution
- - up to 1.4 fold
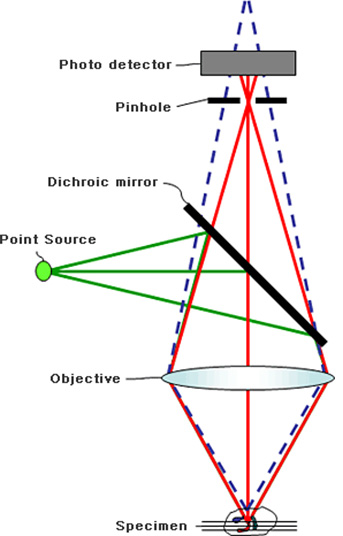
The fundamental principle of a confocal microscope is to obtain images (or signals) of focus from the detector part.
As shown in the figure, where one point of a sample is illuminated and the light reflected from the sample tries to be obtained by the detector, not only light of one point is obtained, but light around it is detected if there is no pinhole.
A confocal microscope that has a pinhole installed in its detection part blocks other kinds of light than the light reflected from an originally intended point so as to obtain signals of one point. As shown in the figure, other kinds of light (dotted line) than the intended light of the point are blocked by the pinhole.
That is the most unique feature of a confocal microscope that obtains signals of one point in a space at a time.
In the structure, a focal point can play a role just as Tip of Stylus, so it is possible to make 3D measurement. In addition, by blocking surrounding light, it is possible to remarkably reduce optical noise and increase microscopic resolution.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) 2D Scan 원리
• Point-by-point imaging : 2D image acquisition
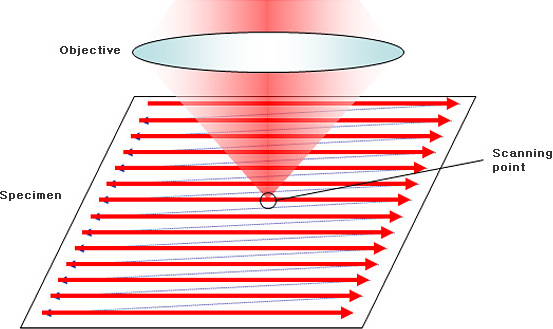
Measuring one point at a time has a limitation in terms of meaningful measurement. To create an image, it is necessary to use a scanning device that can obtain such point data continuously.
In the condition where Tip of Stylus stays put, it is impossible to make profile measurement. Therefore, it is as if Tip is moved over the surface of an object to measure.
2D scanning has three types (see the next page). Of them, beam scanning type is the most effective. Our company as well as high-performance confocal microscope firms including Olympus and Keyence adopts beam scanning type.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) 기본 원리
• Point-by-point imaging : 2D image acquisition

2D scanned image turns into a complete 3D scanned one through the optical axis direction Z scanning process.
In comparison with Stylus Tip, Stylus Tip has a contact type. The vertical position of Tip changes depending on the curve of the surface shape.
On contrast, a confocal microscope has an optical non-contact type. Moving in the Z-axis direction, it observes a signal in each Z-axis scanning height and therefore obtains 3D information.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) 3D Profiler
• Ideally, signal is detected only when the focus is on the surface

Generally, a metal sample never transmits light so that a signal can be obtained on its surface. If a signal is
extracted from the surface, the function of Profiler is executed.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) 영상비교
-
 Image of general microscope
Image of general microscope
-
 Image of confocal microscope
Image of confocal microscope

Of optical measurement devices, a confocal microscope has the most excellent 3D image resolution.
In combination of cross-sectional images, it is possible to turn them into clear 3D images. As shown in the above photo, the images are very clear.
